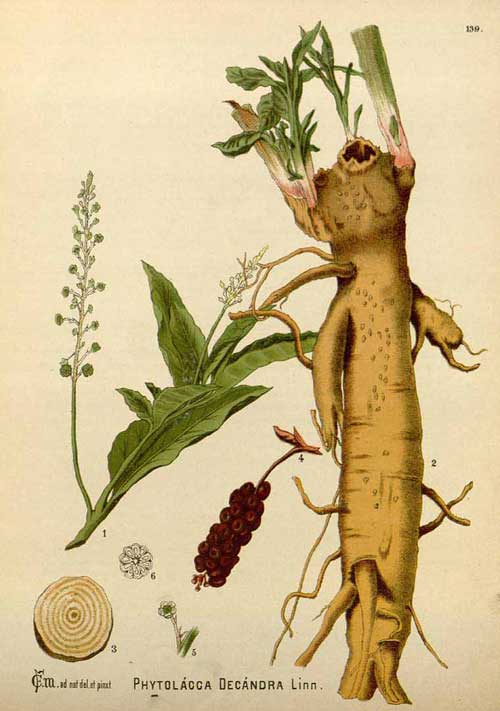
Poke Root – Phytolacca decandra
Poke Root (Phytolacca decandra) is also known as Poke, Poke Berry, Poke Root, Poke Weed, Red-Ink Plant and Shang Lu in Chinese Uses of Poke Root:- Poke Root is a pungent bitter herb, often used in the treatment of arthritis but it is a very potent herb. Poke Root is very full of detoxifying properties and it is an excellent herb for purifying the blood and maintaining lymphatic health. It is anti inflammatory which is why it is typically used with arthritic and rheumatoid conditions. A topically applied decoction of the herb was once, and is still sometimes used, as a home remedy...
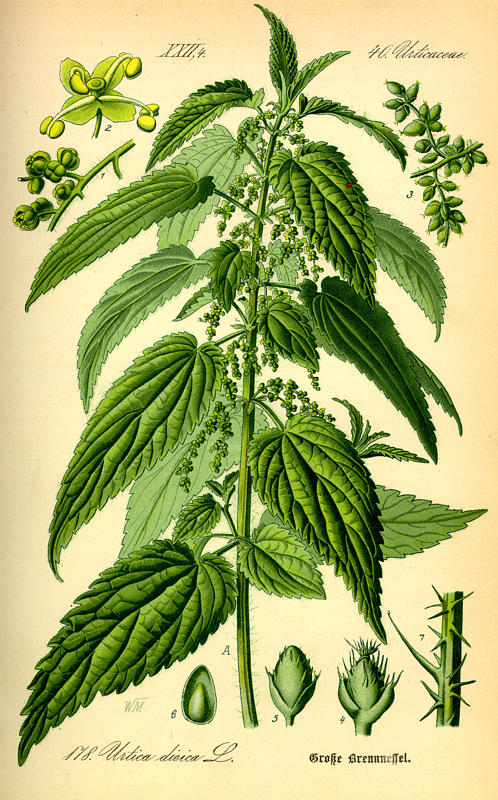
Nettle Seed – Urtica doica
Nettle Seed (Urtica dioica) is sometimes known as Stinging Nettle or Common Nettle. It is a perennial plant native to Europe, Asia and Africa and some parts of the USA. Five of the six subspecies sting with hypodermic like needles which inject histamine and other chemicals when in contact with skin. There are over 500 species of nettles, some of which have a sting so bad, it lasts for months and may cause death. The plant grows to 2 or 3 feet and in covered with down as well as stinging hairs. The leaves are heart-shaped and come to a point. The...
Myrtle Leaves – Myrtus communis
Myrtle Leaves come from the common Myrtle. Sometimes known as True Myrtle which is a native all across the Mediterranean, particularly on Corsica and Sardinia. Not to be confused with the only other Myrtle (Myrtus Nivellei) which is better known as Saharan Myrtle Constituents of Myrtle Leaves:- Myrtle Leaves (Myrtus communis) are very rich in polyphenols. In particular, galloyl-glucosides, ellagitannins, galloyl-quinic acids, flavonol glycosides and hydrolysable tannins (galloyl-glucosides, ellagitannins, galloyl-quinic acids). Myrtle extracts have a potent antioxidant activity mainly due to the presence of galloyl derivatives. Myrtle leaves as well as the volatile oil (Myrtii Oleum; MO) obtained from the...
Irritable Bowel Syndrome or IBS
Irritable Bowel Syndrome or IBS has variable symptoms and medical professionals classify Irritable Bowel Syndrome patients according to a few different sub-types. Although all patients must meet Rome III criteria for diagnosis, their predominant bowel symptom will determine their sub-type. The first two sub-types are self-explanatory: Constipation Predominant IBS (IBS-C) Diarrhoea Predominant IBS (IBS-D) The third sub type is reserved for individual whose symptoms swing from Diarrhoea to Constipation IBS Alternating Type (IBS-A), also known as IBS-Mixed (IBS-M) Many cases of Irritable Bowel Syndrome are self diagnosed or diagnosed by a professional with a kind of throw away explanation of...