Fenugreek Leaves – Trigonella foenum-graecum
£4.50
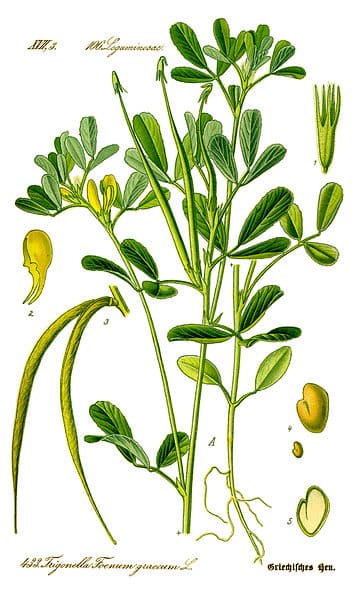
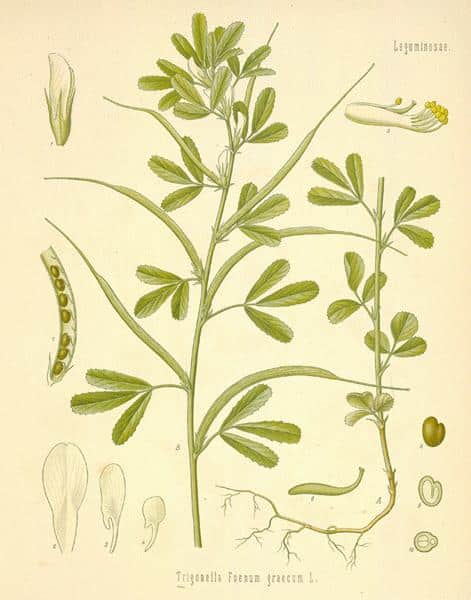
Fenugreek Leaves
Trigonella foenum-graecum
Also known as Methi, Abesh, çemen
100 grams
Trigonella foenum-graecum from which Fenugreek is obtained belongs to the family Fabaceae. It is used both as an herb (the leaves) and as a spice (the seed). It is cultivated worldwide as a semi-arid crop.
Traditional Culinary & Medicinal Uses for Fenugreek:-
Fresh or dried, the leaves are an ingredient in some Indian curries. The young leaves and sprouts of the plant are eaten as greens and the fresh or dried leaves are used to flavour other dishes. The dried leaves kasuri methi have a bitter taste and a strong characteristic smell.
The rhombic yellow to amber coloured seed, commonly called Methi, is frequently used in the preparation of pickles, curry powders and pastes, and is often encountered in the cuisine of the Indian subcontinent.
In India, the seeds are mixed with yoghurt and used as a conditioner for hair. It is also one of the ingredients in the making of khakhra, a type of bread. It is used in injera/taita, a type of bread unique to Ethiopian and Eritrean cuisine.
The word for Fenugreek in Amharic is Abesh, which is also often used as a natural herbal medicine in the treatment of diabetes. It is also sometimes used as an ingredient in the production of clarified butter (Amharic: qibé, Ethiopian and Eritrean Tigrinya: tesme), which is similar to Indian ghee.
In Turkey, the plant gives its name, çemen, to a hot paste used in pastirma. In Yemen it is the main condiment and an ingredient added to the national dish called saltah. The similarity between the Arabic word hulba and the Mandarin Chinese word hu lu ba reveals the significance of the herb and spice in history. Fenugreek is also one of four herbs used for the Iranian recipe Ghormeh Sabzi.
It is mainly used as digestive aid. It is ideal for treating sinus, lung congestion, reduces inflammation and fights infection. The seed is widely used as a galactagogue (milk producing agent) by nursing mothers to increase inadequate breast milk supply. It has also been used to increase breast size. It can be found in capsule form in many health food stores.
Constituents of Fenugreek:-
Fenugreek is a rich source of the polysaccharide galactomannan. It is also a source of saponins such as diosgenin, yamogenin, gitogenin, tigogenin, and neotigogens. Other bioactive constituents of fenugreek include mucilage, volatile oils, and alkaloids such as choline and trigonelline.
A side effect of consuming even small amounts of fenugreek (even as just an infusion in water) is a maple syrup or curry smell in the eater’s sweat and urine which is caused by the potent aroma compound sotolone. Fenugreek is frequently used in the production of flavouring for artificial syrups. The taste of toasted fenugreek is additionally based on substituted pyrazines, as is cumin. By itself, it has a somewhat bitter taste.
History of Fenugreek:-
Fenugreek has a long history as both a culinary and medicinal herb in the ancient world. It was one of the spices the Egyptians used for embalming, and the Greeks and Romans used it for cattle fodder (hence the Latin foenum graecum meaning Greek hay). It was grown extensively in the imperial gardens of Charlemagne.
| Country of Origin | India |
|---|---|
| Batch Code | RD22587969 |
| Harvest | Summer 2023 |
| Best Before | Dec 26 |